PB stability analysis of the case s17 for the KSTAR discharge 7328
The stability analysis of the KSTAR discharge 7328 is presented below. The initial settings for this study are based on the pedestal parameters and other plasma parameters that are outlined in the case s17.
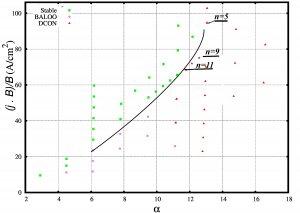
The ballooning stability boundary is shown on this plot. The peeling stability boundary is also identified. However, the parallel current density that will make the peeling modes unstable are significantly large and are in the range of . The
and
toroidal mode numbers that are close to the experimentally observed modes are marked on the diagram. Note, the transition from
to
will be associated with very small changes in the normalized plasma density and with relatively large changes in the parallel current density. The pedestal plasma density for both equilibria was
, the pedestal temperatures were
and
for the cases of
and
unstable modes correspondingly. The bootstrap current was computed using the Sauter formula for the case of
mode and using the Sauter formula with the scaling factor of 1.2 for the case of
mode.
If the values of the plasma temperatures is on the upper boundary of the experimental error bar (or slightly above the error bar), the likely conclusion is that the Sauter formula for KSTAR pedestal parameters under-predicts the bootstrap current.
